Introduction to Customer Experience Management (CXM)
Customer Experience Management (CXM) is a holistic approach that focuses on enhancing every customer interaction to build stronger relationships and drive brand loyalty. It integrates data, technology, and customer insights to create personalized, seamless experiences across multiple touchpoints—from initial awareness to post-purchase engagement. Effective CXM goes beyond customer service; it ensures that every brand interaction aligns with customer expectations, fostering trust, satisfaction, and long-term retention.
In an era where consumers demand efficiency, personalization, and consistency, businesses across industries—from retail and SaaS to healthcare—must leverage CXM strategies to remain competitive. By utilizing AI-driven analytics, customer feedback loops, and omnichannel engagement, brands can proactively address pain points, optimize touchpoints, and create experiences that not only meet but exceed customer expectations.
Evolution of Customer Experience Management
Over time, customer experience management has evolved from basic customer service functions into a sophisticated discipline. Previously, companies would focus on delivering a good product, but in the digital age, it’s more about creating an experience that resonates with customers on an emotional level. From understanding customer journeys to utilizing data-driven insights, CXM has become a major driver for growth in modern businesses.
CXM or CEM: What’s the Difference?
You might come across two terms—CXM and CEM—both of which stand for Customer Experience Management. Historically, CEM (Customer Experience Management) was the common term, focusing more on managing customer feedback and responses to interactions. However, in recent years, CXM (Customer Experience Management) has become the preferred term, signaling a shift toward a more proactive, technology-driven approach.
CXM reflects a more integrated and forward-thinking methodology that uses data, customer journey mapping, and real-time interactions to enhance customer satisfaction. Businesses across industries, from SaaS to retail, are increasingly adopting CXM to improve how they manage their customers’ experiences.
The terminology shift underscores the growing importance of data and technology in shaping customer experiences. While CEM was more reactive, focusing on managing post-interaction feedback, CXM looks at the entire customer lifecycle, from initial awareness to advocacy.
Understanding the Customer Journey
The customer journey refers to the entire experience a customer has with a business, from the first point of contact to becoming a loyal customer. Across industries, understanding and mapping this journey is essential for improving customer experience.
Here are the key stages of a typical customer journey:
- Awareness: The customer first learns about your brand through marketing, advertising, or word of mouth.
- Consideration/Interest: The customer evaluates your product or service, comparing it with alternatives.
- Purchase: The customer decides to buy, influenced by the quality of their experience so far.
- Post-Purchase/Retention: After the purchase, maintaining positive interactions through follow-up communication, support, or loyalty programs is key.
- Advocacy: A satisfied customer becomes a brand advocate, sharing their positive experience with others.
Key Touchpoints
Every industry has critical moments, or touchpoints, when a customer interacts with your brand. These could be visiting your website, using your app, receiving customer support, or interacting with your social media channels. Mapping these touchpoints helps businesses identify where they are excelling and where they should improve.
Customer Expectations and Perceptions
Customers today expect personalized, seamless experiences across all industries. Whether they’re booking a hotel, subscribing to a software service, or shopping for groceries online, the expectation is the same: speed, convenience, and personalization. Businesses that fail to meet these expectations risk losing customers to competitors who do.
Components of Effective Customer Experience Management
Delivering an exceptional customer experience requires businesses to focus on several key components that are universally applicable across industries:
1. Personalization
Customers now expect highly tailored experiences. Whether you’re a healthcare provider offering personalized care plans or a SaaS company customizing product features, personalization is critical to improving engagement and satisfaction. For instance, Spotify offers personalized playlists based on user listening habits, enhancing the customer experience through relevant recommendations.
2. Omnichannel Experience
Consistency across all platforms is crucial. Whether a customer interacts with your business in-store, through a website, or via a mobile app, the experience should be smooth and unified. IKEA, for example, integrates its physical stores with its online platform, allowing customers to check inventory online before visiting a store, ensuring a seamless omnichannel experience.
3. Employee Engagement
Engaged employees are key to delivering superior customer service. Training staff to be responsive, knowledgeable, and proactive can significantly improve the customer experience. For example, Southwest Airlines is known for its strong employee engagement, which translates into exceptional service and customer satisfaction.
4. Technology Integration
Integrating technology into CXM helps businesses gather customer insights, automate responses, and enhance interactions. Whether using AI chatbots for customer service or customer data platforms (CDPs) for personalized marketing, technology plays a vital role in improving customer experience. Salesforce, enables companies to streamline interactions and manage customer data effectively, leading to enhanced CX.
Measuring Customer Experience
Businesses need to measure customer experience effectively to improve it. Across industries, tracking and analyzing the right metrics can help companies understand how customers perceive their interactions with the brand and identify areas for improvement.
Here are some key metrics for measuring customer experience:
1. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The NPS is a widely used metric that measures customer loyalty by asking one simple question: “How likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague?” Customers respond on a scale from 0 to 10, and the results are classified into promoters (9-10), passives (7-8), and detractors (0-6). A higher NPS indicates strong customer loyalty and satisfaction. This metric is used across industries, from healthcare to financial services, to gauge overall customer sentiment.
2. Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
CSAT measures how satisfied customers are with a specific interaction, product, or service. It’s typically measured through a follow-up survey that asks customers to rate their satisfaction on a scale from 1 to 5 or 1 to 10. For example, after a product purchase, an e-commerce company might ask customers to rate their experience with the checkout process, product delivery, or customer support.
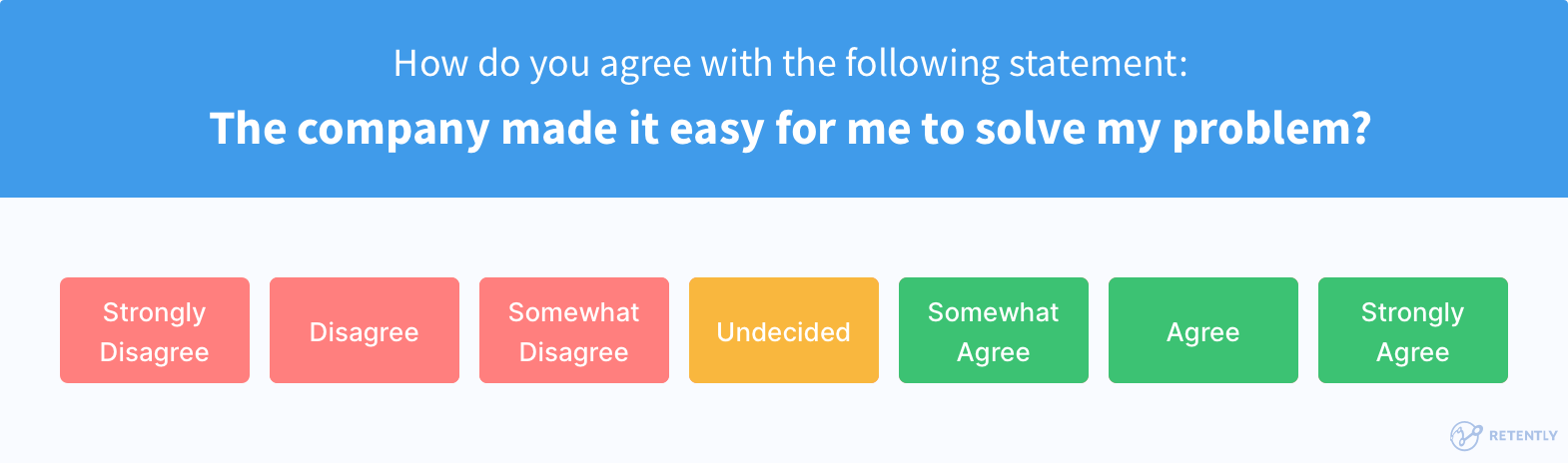
3. Customer Effort Score (CES)
CES measures how easy it is for customers to complete a task, such as making a purchase, resolving an issue, or finding information. Usually, customers are asked to respond to a statement like “[Name of the organization] made it easy for me to handle [issue]” with a 1-5 or 1-7 scale rating, where 1: strongly disagree and 5 or 7: strongly agree. The less effort required, the better the CES—and, arguably, the higher the customer satisfaction.The lower the effort required, the better the customer experience. Companies like American Express have used CES to improve customer service, finding that reducing effort is directly correlated with increased loyalty.
Read more about the differences and similarities between NPS, CSAT, and CES.
Tools and Technologies for measuring
Businesses today use a range of tools and technologies to track and measure customer experience. Customer feedback tools like Omniconvert, SurveyMonkey, and Medallia are popular for gathering direct feedback, while analytics platforms like Google Analytics or Hotjar can help monitor customer behavior across digital channels. Remember that you can’t improve what you cannot measure.
Strategies for Improving Customer Experience
Improving customer experience requires a combination of strategic planning and ongoing optimization. Whether you’re in e-commerce, SaaS, healthcare, or financial services, focusing on the following strategies can help you create a customer-centric organization:
1. Design a Customer-Centric Culture
A customer-centric culture prioritizes the needs and preferences of customers in every decision. This culture should start at the top, with leadership driving the commitment to customer experience, and trickling down through every department. For instance, Nordstrom, a leading retailer, has built its reputation on putting customers first, with flexible return policies and exceptional in-store service.
2. Invest in Employee Training
Well-trained employees are critical to delivering excellent customer experiences. Companies should focus on developing the skills and empathy needed to resolve customer issues and provide personalized support. Training programs that teach active listening, problem-solving, and product knowledge can significantly enhance service quality. Ritz-Carlton is famous for its employee training programs, which empower staff to take the initiative in exceeding customer expectations.
3. Implement Continuous Feedback Loops
Gathering and acting on customer feedback is crucial for continuous improvement. Companies should establish feedback loops where customer input is consistently reviewed and used to refine processes, services, and products. Adobe, for instance, regularly collects feedback from users to make incremental improvements to its cloud-based design tools, ensuring customer needs are met effectively.
4. Leverage Data and Analytics
Data is at the heart of understanding customer behavior and improving the overall experience. Companies should use analytics to track customer journeys, preferences, and feedback in real-time. Tools like Salesforce or HubSpot help businesses gather, analyze, and act on customer data to create more personalized experiences. In industries like retail and travel, predictive analytics are increasingly being used to anticipate customer needs and offer tailored experiences.
5. Optimize Digital Touchpoints
As businesses continue to shift online, optimizing digital touchpoints—such as websites, apps, and social media—is essential. Whether it’s streamlining the checkout process in an e-commerce platform or improving navigation in a SaaS application, enhancing digital experiences can significantly boost customer satisfaction and reduce churn.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Improving Customer Experience
While businesses strive to improve customer experience, several common pitfalls can undermine these efforts:
1. Failing to Align Internal Teams
One of the biggest mistakes companies make is not ensuring that all departments are aligned around the customer experience strategy. When teams—such as marketing, sales, and customer service—are not working toward the same CX goals, the result can be a fragmented and inconsistent experience for customers.
2. Neglecting Employee Experience
A company’s employees are critical to delivering excellent customer experiences. However, many businesses focus so heavily on customer satisfaction that they forget to support their employees. Employee dissatisfaction can directly impact service quality, leading to poor customer interactions. Empowering and engaging employees through proper training, recognition, and resources is crucial for ensuring a positive CX.
3. Overlooking Data and Feedback
Another common mistake is ignoring or not acting on customer feedback. Some businesses collect feedback but fail to analyze it or implement changes based on customer insights. Similarly, companies that don’t make data-driven decisions risk losing touch with what their customers need or expect.
4. Focusing on Technology Over Human Interaction
While technology is an essential tool in CXM, businesses should avoid relying too heavily on automation at the expense of personal, human interaction. Automated solutions like chatbots or AI-powered customer service tools can be highly efficient but may lack the empathy or personalization that customers appreciate. Balancing technology with human touchpoints is key to delivering a well-rounded experience.
5. Ignoring the Customer Journey
Businesses often focus on specific touchpoints, like sales or post-purchase support, without considering the entire end-to-end customer journey. Improving CX requires understanding how each interaction—before, during, and after a sale—contributes to the overall experience. Focusing on isolated stages can lead to gaps in service or disjointed customer experiences.
To wrap things up
Customer Experience Management (CXM) is essential for any business aiming to thrive in today’s competitive landscape, regardless of industry. Delivering exceptional customer experiences at every touchpoint helps build trust, foster loyalty, and drive long-term growth. By investing in key components such as personalization, omnichannel consistency, and employee engagement—and leveraging the right tools and data—businesses can effectively manage and enhance their customer relationships.
The customer journey is no longer linear, making it even more crucial to map and understand your customer’s expectations and perceptions across various channels. Consistently measuring and optimizing customer experiences through tools like NPS and CES ensures that companies remain responsive to customer needs.
By prioritizing CXM, businesses can not only improve customer satisfaction and retention but also gain a competitive edge in an increasingly customer-centric world.
FAQs
What are the benefits of Customer Experience Management (CXM)?
Effective CXM leads to several benefits, including improved customer satisfaction, increased loyalty, higher lifetime value, and positive word-of-mouth marketing. Businesses that invest in CXM see better retention rates and increased customer advocacy, which can drive growth and profitability across all industries.
What is the difference between CRM and CXM?
While both Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Customer Experience Management (CXM) focus on customer interactions, they differ in scope. CRM is more about managing relationships and data, such as tracking customer information and sales history. CXM takes a broader view, focusing on the entire customer journey and the quality of each interaction, from first contact to post-purchase support.
What are some challenges in CXM?
Some common challenges in CXM include handling fragmented customer data, ensuring consistency across multiple channels, and adapting to rapidly changing customer expectations. Additionally, industries like retail or hospitality face the difficulty of integrating online and offline experiences, while SaaS companies might struggle with creating seamless onboarding experiences for new users.